What is Service in Kubernetes?
A Kubernetes Service is an
abstractionwhich defines a logical set of Pods running somewhere in your cluster, that all provide the same functionality. When created, each Service is assigned aunique IP address (also called clusterIP).This
addressis tied to thelifespan of the Service, and will not change while the Service is alive. Pods can be configured to talk to the Service and know that communication to the Service will be automatically load-balanced out to some pod that is a member of the Service.
Types of Services in Kubernetes:
Visual Representation of Services in Kubernetes:
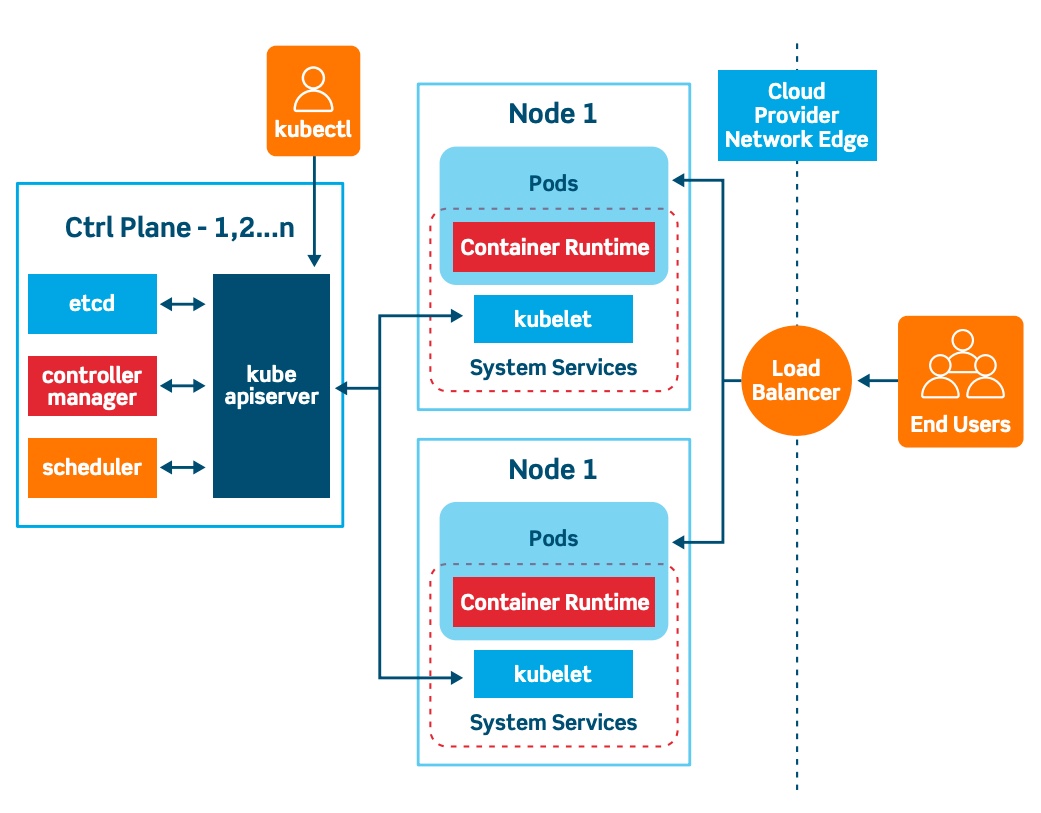
So before starting the task let's do necessary installation and setup.
- Before Doing the task let's set up the git repository for the same and push the code to the repository.
Steps to follow: Here we will use AWS for Deployment and Git for version control.
Step-01: Open your terminal or any other cloud service.
Step-02: Update and install Docker on your machine.
sudo apt update
sudo apt install docker.io
Step-03: Now give Docker permission for super user of your local machine.
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER && newgrp docker
Step-04: Now let's install Minikube.
curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/minikube/releases/latest/minikube-linux-amd64
sudo install minikube-linux-amd64 /usr/local/bin/minikube
Step-05: Now let's start Minikube.
minikube start
- let's connect with docker.
minikube start — driver=docker
Step-06: Now let's check the status of Minikube.
minikube status
Step-07: Now we will install the Command line instruction for Minikube which is Kubectl.
- But first, install snap on your machine.
sudo apt install snap
- CLI for Minikube is Kubectl.
sudo snap install kubectl --classic
Step-08: Now let's check the version of Kubectl
kubectl version
Step-09: Now Clone the repository from the github. Github Repo link : github.com/LondheShubham153/django-todo-cic..
git clone https://github.com/LondheShubham153/django-todo-cicd.git
Step-10: Now let's check the files in the repository.
ls
cd django-todo-cicd
Task-1:
- Create a Service for the deployment.
Step-01: Create a file service.yaml and write the code for the service.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: django-todo-services
namespace: python-django-app
spec:
type: NodePort
selector:
app: django-app
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 8000
targetPort: 30007
- Now let's create a namespace first for the deployment.
kubectl create namespace python-django-app
- As we have created services and namespace now lets create a deployment.
Syntax: kubectl create -f <filename> -n <namespace>
kubectl create -f service.yaml -n python-django-app
- Now verify the deployment and service.
kubectl get all -n python-django-app
Task-2:
- Create a ClusterIP service for the deployment.
Step-01: Create a file clusterip-service.yaml and write the code for the service.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: django-todo-services
namespace: python-django-app
spec:
type: NodePort
selector:
app: django-app
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 8000
targetPort: 8000
type: ClusterIP
- Now let's create a deployment.
Syntax: kubectl create -f <filename> -n <namespace>
kubectl create -f clusterip-service.yaml -n python-django-app
- Check of the Service is created or not.
kubectl get svc -n python-django-app
- Now verify the deployment and service.
kubectl get all -n python-django-app
Task-3:
- Create a LoadBalancer service for the deployment.
step-1: Create a file loadbalancer-service.yaml and write the code for the service.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: django-todo-lb-services
namespace: python-django-app
spec:
type: NodePort
selector:
app: django-app
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 8000
targetPort: 8000
type: LoadBalancer
- Now let's create a deployment.
syntax:kubectl create -f <filename> -n <namespace>
kubectl create -f loadbalancer-service.yaml -n python-django-app
- Check of the Service is created or not.
kubectl get svc -n python-django-app
minikube service list
- Now verify the deployment and service.
kubectl get all -n python-django-app



